Agricultural Pesticides and Sustainable Farming in the United States
 Home Page Home Page  News & Events News & Events |
The Role of Pesticides in Agricultural Production
Pesticides play a critical role in controlling insects, diseases, and weeds that threaten crop quality. Proper pesticide use enhances crop yields and product quality, bolstering the U.S. agricultural economy and food security. Yet, improper or excessive use can cause environmental and health issues.
Environmental Challenges Linked to Pesticides
The U.S. faces significant environmental concerns from intensive pesticide use, especially in high-production farming areas. These include groundwater and surface water contamination, adverse effects on biodiversity, and the development of pest resistance to conventional pesticides.
Sustainable Farming as an Integrated Approach
Sustainable agriculture emphasizes farming practices that protect natural resources and the environment without compromising productivity. In this context, the U.S. employs strategies such as:
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): A balanced approach combining biological, cultural, and chemical methods to reduce reliance on pesticides.
- Use of Eco-friendly Pesticides: Less toxic, biodegradable pesticides that minimize environmental risks.
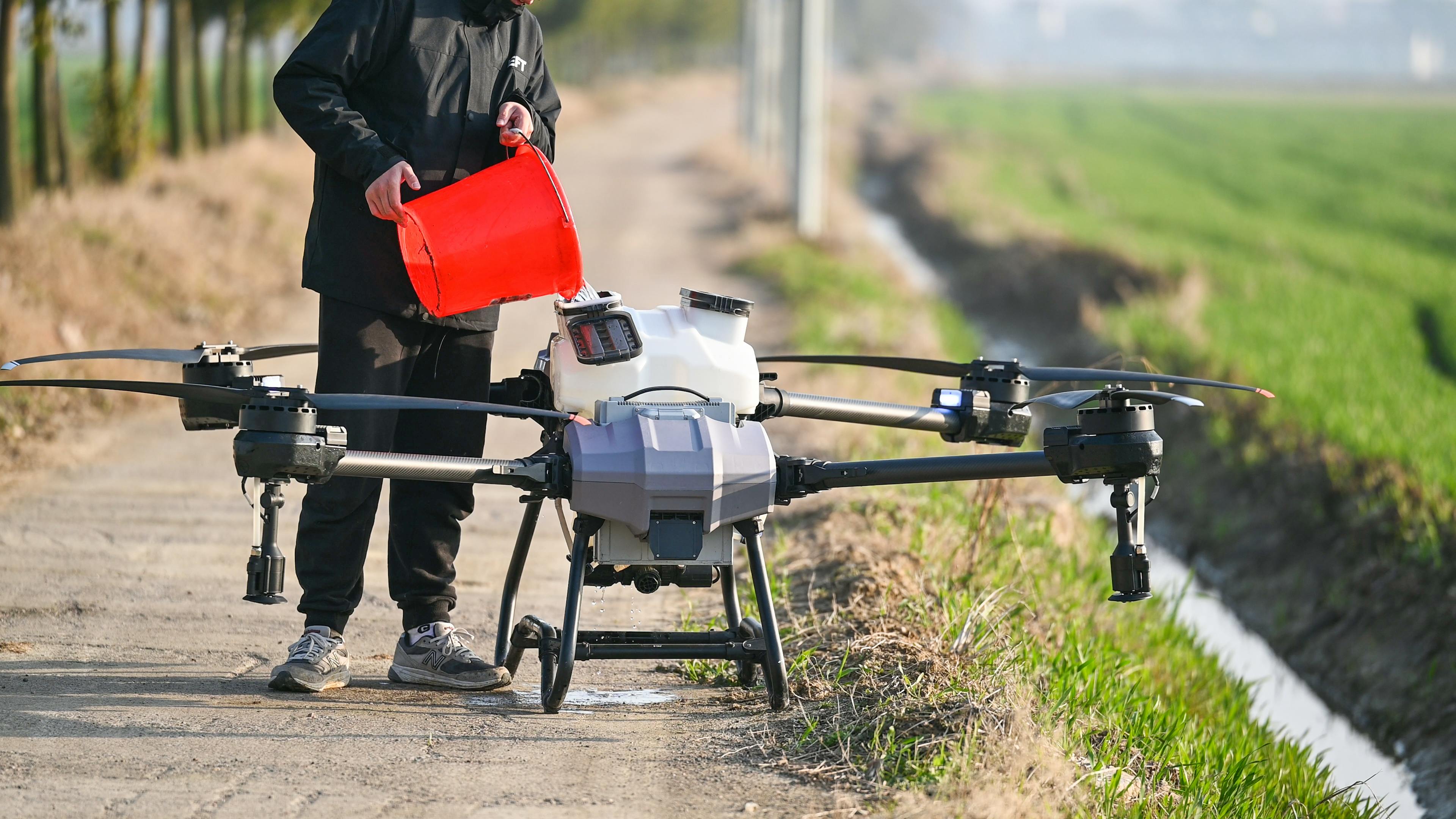
- Modern Technologies: Smart spraying, drones, and sensors help apply pesticides precisely and efficiently.
U.S. Policies and Regulations
The United States operates under a strict regulatory framework overseen by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to ensure pesticide use safeguards public health and the environment. The EPA assesses safety, registers pesticides, enforces limits on dosages and application timing, and monitors environmental impacts .
Balancing Production with Environmental Protection
The main challenge lies in achieving sustainable, high-quality agricultural output while minimizing environmental harm. Farmers and scientists focus on improving pesticide use methods, developing biological alternatives, and promoting organic and semi-organic farming practices.
Conclusion
Through responsible pesticide use and sustainable practices, the U.S. aims to balance food security with environmental protection, reflecting a forward-looking vision to preserve natural resources for future generations.





