Using Drones for Pesticide Spraying
 Home Page Home Page  News & Events News & Events |
Agriculture in the United States is undergoing a technological revolution with the adoption of drones as efficient tools for pesticide spraying. This modern technology improves spraying precision, reduces chemical usage, and minimizes environmental damage, making it a sustainable and advanced choice aligned with modern farming demands.

Advantages of Using Drones for Pesticide Spraying
- High Precision: Drones can spray pesticides with exceptional accuracy, targeting only affected areas and avoiding unnecessary chemical use.
- Effectiveness in Difficult Terrain: They can reach areas that are hard for tractors or workers to access, such as hills and rugged landscapes.
- Time and Labor Savings: Compared to traditional methods, drones speed up spraying operations significantly, enabling faster field monitoring and quicker response to issues.
- Reduced Worker Exposure: Using drones reduces the need for workers to be physically present during spraying, improving occupational safety.
How Do Drones Work for Pesticide Spraying?
Drones employ advanced systems like high-resolution cameras, environmental sensors, and data analytics software to identify areas needing treatment. They can be programmed for autonomous missions, with manual control options available to ensure optimal results.
Applications and Examples in the United States
- States like California and Florida have seen large farms adopt drones for spraying pesticides in citrus and vegetable fields.
- Companies such as DJI and PrecisionHawk offer specialized agricultural drones equipped with advanced spraying monitoring technologies.
- Drones are integrated into many farms’ Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies across the U.S.
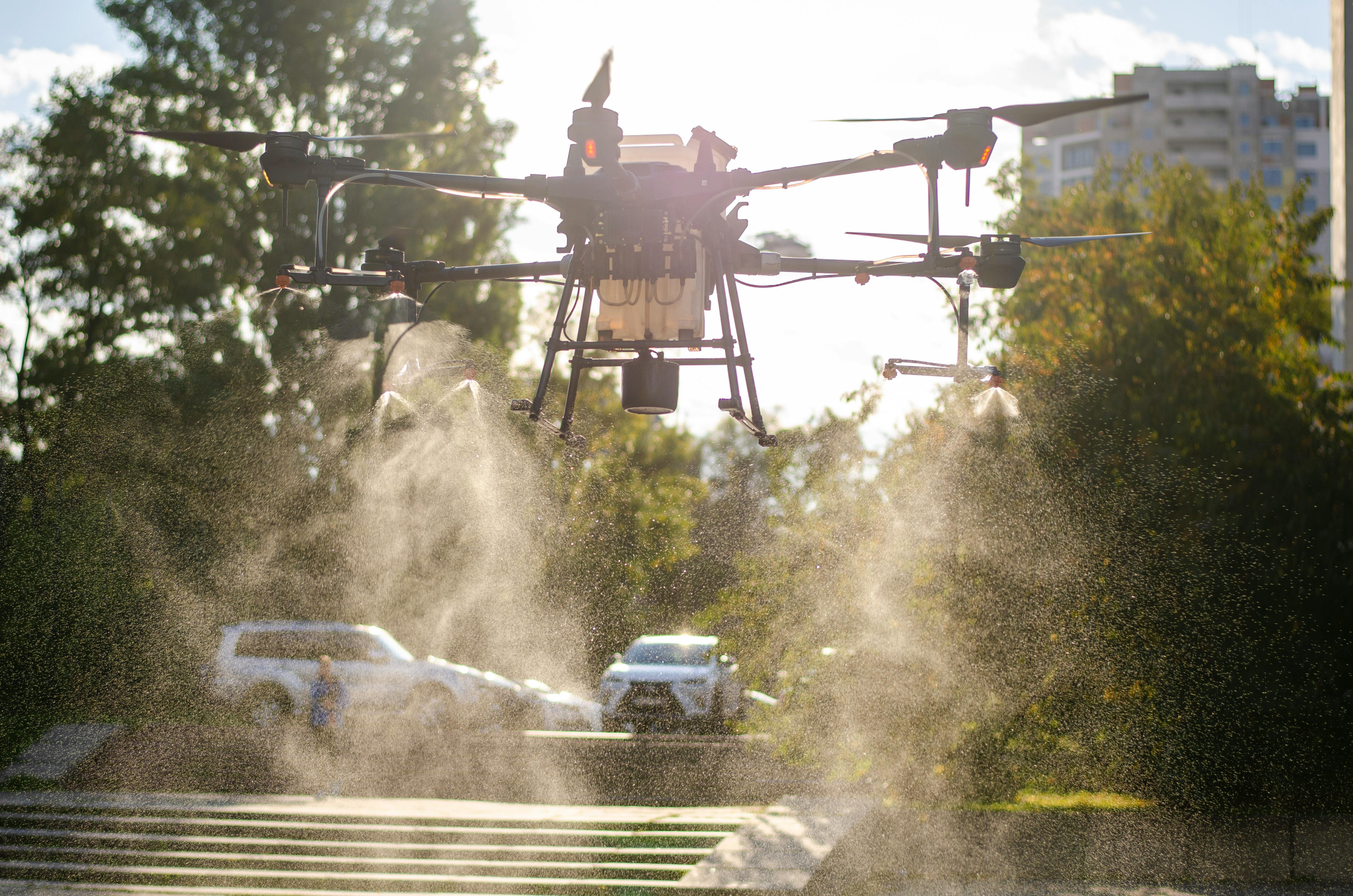

Challenges and Considerations
- Initial Costs: Although decreasing, the purchase and operation costs of drones remain a barrier for some farmers.
- Regulations: Drones are subject to strict rules by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), which must be followed to ensure safety.
- Operator Training: Skilled operators require specialized training to effectively pilot and program drones.
Future Trends
With ongoing advances in AI and remote sensing, drones are expected to expand their roles to include plant health monitoring, smart fertilization, and precision irrigation, enhancing agricultural sustainability and reducing costs.